고래씌
[JAVA] 8. 객체 배열 & 실습문제 본문
1. 객체 배열
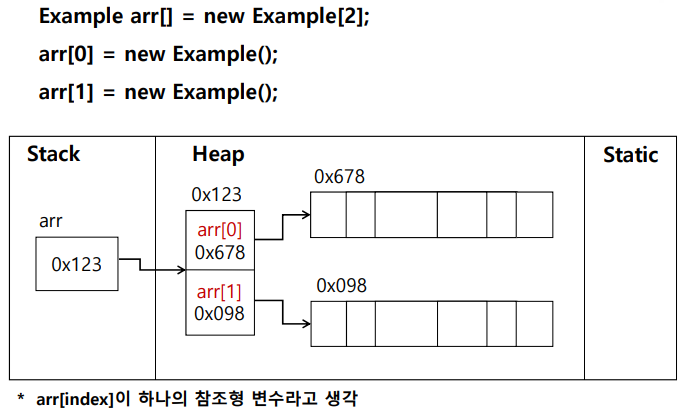
=> 객체 배열을 생성할 때 Heap 메모리 안에 무조건 들어간다!
Alt + Shift + s 단축키 => Generate Getters and Setters
package com.kh.chap01_oneVsMany.mdoel.vo;
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
private int price;
private String publisher;
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getPublisher() {
return publisher;
}
public void setPublisher(String publisher) {
this.publisher = publisher;
}
public Book(String title, String author, int price, String publisher) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.publisher = publisher;
}
public Book() {
}
public String information() {
return title+ ", " + author + ", " + price + ", " + publisher;
}
}package com.kh.chap01_oneVsMany.run;
import java.util.Scanner;
import com.kh.chap01_oneVsMany.mdoel.vo.Book;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 기본생성자를 호출하여 객체 생성후 setter메소드를 통해 각 필드에 값을 대입
Book bk1 = new Book();
bk1.setTitle("Do it 자바프로그래밍");
bk1.setAuthor("라이언");
bk1.setPrice(25000);
bk1.setPublisher("이지스 퍼블리싱");
System.out.println(bk1.information());
// 2. 매개변수 생성자로 객체 생성과 동시에 필드에 값을 대입
Book bk2 = new Book("자바프로그래밍 입문", "전예홍", 25000, "이지스 퍼블리싱");
// 3. 3개의 Book 객체가 필요하다는 가정하에 각각의 book 객체를 별도로 관리.
// 단, 각 Book 객체는 사용자에게 입력받은 값들로 채워넣을 예정
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Book bk4 = null;
Book bk5 = null;
Book bk6 = null;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++) { // 이렇게 하면 book객체 1개 밖에 관리를 못함.
System.out.print("제목 : ");
String title = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("저자 : ");
String author = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("가격 : ");
int price = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("출판사 : ");
String publisher = sc.nextLine();
if(i == 0) {
bk4 = new Book(title, author, price, publisher);
}else if(i == 1) {
bk5 = new Book(title, author, price, publisher);
}else {
bk6 = new Book(title, author, price, publisher);
} // => 이런 코드는 유지보수가 어려움. 데이터가 많을 수록 관리가 어려움
// 반복문 동시에 변수를 설정하면 반복문 끝남과 동시에 사라짐
}
}
}☞ 안에 for문은 대량의 데이터를 저장하고 관리할 때 유지보수가 어렵다! 그래서 객체 배열을 이용
☞ 그러므로 아래와 같이 객체 배열을 사용해주어야 한다!
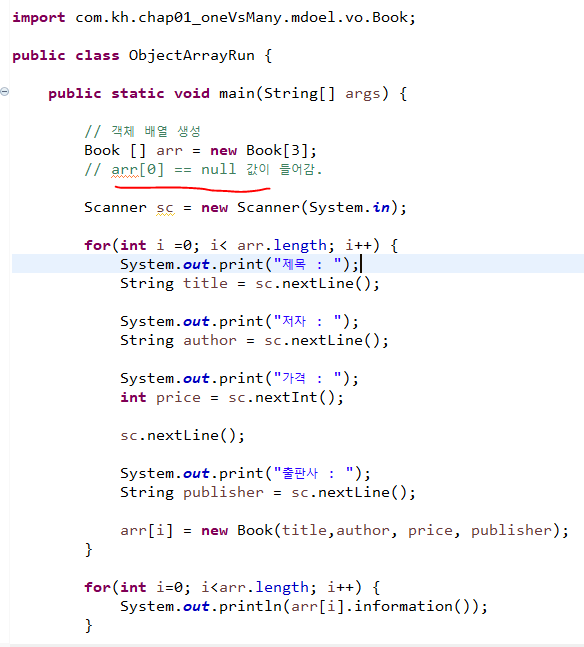
- Book 객체 배열은 참조형임!
- 그래서 값이 안들어간 arr[0] 은 null 값이 들어가 있음
package com.kh.chap01_oneVsMany.run;
import java.util.Scanner;
import com.kh.chap01_oneVsMany.mdoel.vo.Book;
public class ObjectArrayRun {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 객체 배열 생성
Book [] arr = new Book[3];
// arr[0] == null 값이 들어감.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i =0; i< arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print("제목 : ");
String title = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("저자 : ");
String author = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("가격 : ");
int price = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("출판사 : ");
String publisher = sc.nextLine();
arr[i] = new Book(title,author, price, publisher);
}
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i].information());
}
// 사용자에게 검색할 도서 제목을 입력받아 전체 도서들의 제목과 일일이 비교하여
// 일치하는 도서의 가격을 알려주는 메소드
System.out.println("검색할 책 제목: ");
String searchTitle = sc.nextLine();
int count = 0;
// 만약 일치하는 도서를 찾지 못한 경우 "검색된 도서가 없습니다" 출력
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i].getTitle().equals(searchTitle)) {
count++;
System.out.println(arr[i].getPrice());
break;
}
}
if(count == 0) System.out.println("검색된 도서가 없습니다.");
}
}
2. 객체배열 실습문제
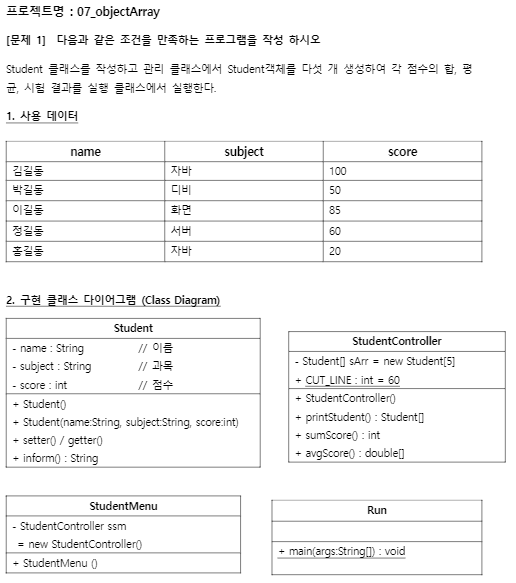



package com.kh.practice.student.model.vo;
public class Student {
private String name;
private String subject;
private int score;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, String subject, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.subject = subject;
this.score = score;
}
public String inform() {
return "이름 : "+name + " / " + "과목 : " +subject + " / " + "점수 : " +score + " ";
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setSubject(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
}package com.kh.practice.student.controller;
import com.kh.practice.student.model.vo.Student;
public class StudentController {
private Student [] sArr = new Student[5];
public static final int CUT_LINE = 60;
public StudentController() {
sArr[0] = new Student("김길동","자바",100);
sArr[1] = new Student("박길동","디비",50);
sArr[2] = new Student("이길동","화면",85);
sArr[3] = new Student("정길동","서버",60);
sArr[4] = new Student("홍길동","자바",20);
// Student s1 = new Student("김길동","자바",100);
// Student s2 = new Student("박길동","디비",50);
// Student s3 = new Student("이길동","화면",85);
// Student s4 = new Student("정길동","서버",60);
// Student s5 = new Student("홍길동","자바",20);
}
public Student[] printStudent() {
return sArr;
}
public int sumScore() {
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<sArr.length; i++) {
sum+= sArr[i].getScore();
}
return sum;
}
public double[] avgScore() {
double [] davg = new double[2];
davg[0] = sumScore();
davg[1] = davg[0] / 5;
return davg;
}
}package com.kh.practice.student.view;
import com.kh.practice.student.controller.StudentController;
import com.kh.practice.student.model.vo.Student;
public class StudentMenu {
private StudentController ssm = new StudentController();
private Student s = new Student();
public StudentMenu() {
System.out.println("========== 학생 정보 출력 ==========");
Student [] stdArr = ssm.printStudent();
for(int i=0; i<stdArr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(stdArr[i].inform());
}
System.out.println("========== 학생 성적 출력 ==========");
System.out.println("학생 점수 합계 : "+ (int) ssm.avgScore()[0]); // 강제형변환
System.out.println("학생 점수 평균 : "+ ssm.avgScore()[1]);
System.out.println("========== 성적 결과 출력 ==========");
for(int i=0; i<stdArr.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%s학생은 %s대상입니다.\n", stdArr[i].getName(),
stdArr[i].getScore() < ssm.CUT_LINE ? "재시험" : "통과 ");
}
}
}package com.kh.practice.student.run;
import com.kh.practice.student.model.vo.Student;
import com.kh.practice.student.view.StudentMenu;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StudentMenu sm = new StudentMenu();
}
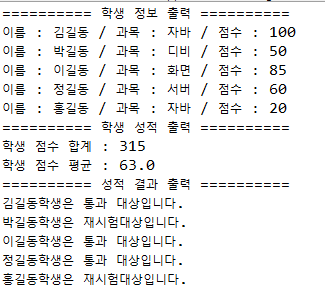
}
'JAVA > JAVA 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 사원 프로그램 객체 실습 (0) | 2023.10.13 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 9. 상속 & 오버라이딩 (0) | 2023.10.13 |
| [JAVA] 7-4. 오버로딩 & 클래스 실습문제 (0) | 2023.10.13 |
| [JAVA] 7-3. 메소드(Method) (0) | 2023.10.12 |
| [JAVA] 7-2. 생성자 (0) | 2023.10.12 |



