고래씌
[JAVA] 11-1. 기본 API(1) (Math 클래스, 문자열) 본문
1. API

=> import java.lang.*; 은 항상 자동으로 모든 클래스 내부에 java.lang패키지 내부의 클래스가 import 되어 있다!
=> 이 패키지 안에는 int, math, System.~ 등의 클래스가 들어있다
1) Math 클래스 관련 기능(수학과 관련된 기능을 제공)
(1) 파이 => Math 클래스 내의 상수필드 3.1415...
Math.PI
메소드명(매개변수) : 반환형
(2) 올림처리 메소드 => Math.ceil(double) : double
(3) 반올림 => Math.round(double) : long (정수값 반환)
(4) 버림 => Math.fllor(double) : double
(5) 가장 가까운 정수값을 알아낸 후 실수형 반환 : rint
Math.rint
(6) 절대값 => Math.abs(int/double/long/float) : 매개변수의 자료형 그대로
(7) 최소값 => Math.min(int, int ) : int
최대값 => Math.max(int, int ) : int
(8) 제곱근(루트) => Math.sqrt(double) : double
(9) 제곱 => Math.pow(double, double) : double
외우는 건 권장 X
package com.kh.chap01_math.run;
// import java.lang.*;
// 생략가능. 보이진 않지만 항상 자동으로 모든 클래스에는 java.lang패키지 내부의 클래스가 import 되어있음
public class MathRun {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Math 클래스 관련 기능(수학과 관련된 기능을 제공)
// 파이 => Math 클래스 내의 상수필드 3.1415....
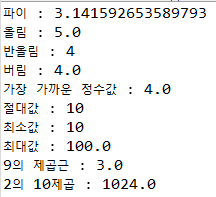
System.out.println("파이 : " + Math.PI);
// 메소드명(매개변수) : 반환형
// 올림처리 메소드 => Math.ceil(double) : double
double num1 = 4.349;
System.out.println("올림 : " + Math.ceil(num1));
// 반올림 => Math.round(double) : long (정수값 반환)
System.out.println("반올림 : " + Math.round(num1));
// 버림 => Math.floor(double) : double
System.out.println("버림 : " + Math.floor(num1));
// 가장 가까운 정수값을 알아낸 후 실수형 반환 : rint
System.out.println("가장 가까운 정수값 : " + Math.rint(num1));
// 절대값 => Math.abs(int/double/long/float) : 매개변수의 자료형 그대로
int num2 = -10;
System.out.println("절대값 : " + Math.abs(num2));
// 최소값 => Math.min(int, int ) : int
System.out.println("최소값 : " + Math.min(10, 100));
// 최대값 => Math.max(int, int ) : int
System.out.println("최대값 : " + Math.max(100, 11.0)); // 100이 double형으로 자동형변환
// 제곱근(루트) => Math.sqrt(double) : double
System.out.println("9의 제곱근 : " + Math.sqrt(9));
// 제곱 => Math.pow(double, double) : double
System.out.println("2의 10제곱 : " + Math.pow(2, 10));
}
}
▶ java.lang.Math 클래스의 특징
- 모든 필드 : 상수필드(PI, E)
- 모든 메소드 : static 메소드
☞ 모든게 다 static이기 때문에 멤버에 접근시 Math.필드 or Math.메소드명으로 다 접근할 수 있다.
즉, 객체를 생성할 필요가 없다.
☞ 따라서 Math클래스의 생성자는 애초에 객체생성이 불가능하도록, private 접근제한자를 가지고 있음
2) String 불변클래스(값이 변하지 않는 클래스)
(1) 값을 수정하는 순간 기존의 값이 담겨있는 공간에서 수정되지 않음
▶ String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = new String("hello"); // hello 객체가 변하지 않고 객체를 새롭게 생성하는 방식
System.out.println(str1 == str2); // false
System.out.println(str1.toString());
// String클래스의 toString()메소드의 경우 실제 담겨있는 문자열을 반환하도록 오버라이딩 되어있음
=> hello 출력
▶ System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); // true
// String클래스의 equals()메소드의 경우 주소값 비교가 아닌 문자열 비교를 하도록 오버라이딩 되어있음
▶ System.out.println(str1.hashCode());
▶ System.out.println(str2.hashCode());
// String클래스의 hashCode()메소드의 경우 주소값 기반이 아닌 실제 담긴 문자열 기반으로 해시코드 값을 반환하도록 오버라이딩 되어있음
▶ 정말 주소값을 알고싶을때 사용하는 메소드. System.identityHashCode(참조변수);
public void method1() {
String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = new String("hello"); // hello 객체가 변하지 않고 객체를 새롭게 생성하는 방식
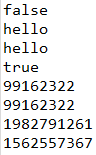
System.out.println(str1 == str2); // false
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str1.toString());
// String클래스의 toString()메소드의 경우 실제 담겨있는 문자열을 반환하도록 오버라이딩 되어있음
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
// String클래스의 equals()메소드의 경우 주소값 비교가 아닌 문자열 비교를 하도록 오버라이딩 되어있음
System.out.println(str1.hashCode());
System.out.println(str2.hashCode());
// String클래스의 hashCode()메소드의 경우 주소값 기반이 아닌 실제 담긴 문자열 기반으로 해시코드
// 값을 반환하도록 오버라이딩 되어있음
// 정말 주소값을 알고싶을때 사용하는 메소드. System.identityHashCode(참조변수);
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str1));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str2));
}
(2) 문자열을 리터럴로 생성
=> 리터럴 값은 상수풀(String pool)에 올라감
=> String pool : 동일한 문자열 존재 불가.
리터럴 값에 보관된 문자열들은 동일한 주소에 저장됨

public void method2() {
String str = new String("hello");
// 리터럴값은 상수풀(String pool)에 올라감
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "hello";
// String pool : 동일한 문자열 존재 불가.
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1.hashCode());
System.out.println(str2.hashCode());
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str1));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str2));
}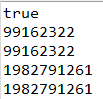
☞ System.identityHashCoder(참조변수) 를 이용하여 출력하였을때 문자열을 리터럴로 대입하였을 때 동일한 주소값이 출력되는 것을 확인
(3) 불변 클래스
public void method3() {
String str = "hello";
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str));
str = "goodbye";
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str));
str += "abc"; // goodbyeabc
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str));
String str2 = "hello";
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str2));
}
3) 문자열
(1) 문자열.charAt(int index) : char
: 문자열에서 전달받은 index의 위치에 있는 문자 하나만 뽑아서 반환(리턴)
ex)
char ch = str1.charAt(4); // o
System.out.println("ch : "+ch);
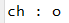
(2) 문자열.concat(String str) : String
: 문자열과 전달된 문자열을 하나로 합쳐서 반환
ex)
String str1 = "Hello World";
String str2 = str1.concat("!!!!!!");
System.out.println(str2);
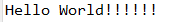
(3) 문자열.length() : int
: 문자열의 길이를 반환
ex)
String str1 = "Hello World";
System.out.println("str1의 길이 : " + str1.length());
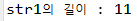
(4.1) 문자열.substring(int beginIndex) : String
: 문자열의 beginIndex위치에서부터 끝까지 문자열을 추출해서 리턴
(4.2) 문자열.substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) : String
: 문자열의 beginIdex의 위치에서부터 endIndex-1까지의 문자열을 추출해서 리턴
ex)
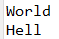
String str1 = "Hello World";
System.out.println(str1.substring(6));
System.out.println(str1.substring(0,4)); // 0 <= 인덱스범위 < 5
(5) 문자열.replace(char old, char new) : String
: 현재 문자열에서 old문자를 new문자로 대체(replace)하고 변환한 문자열 리턴
ex)
String str1 = "Hello World";
String str3 = str1.replace('l', 'a');
System.out.println("str3 : " +str3);

(6) 문자열.trim() : String
: 문자열의 앞 뒤 공백을 제거한 문자열 리턴
ex)
String str4 = " J A V A ";
System.out.println("trim() : "+str4.trim()); // J A V A
System.out.println("trim() : "+str4.trim().replace(" ", "")); // JAVA

(7.1) 문자열.toUpperCase() : String
: 문자열을 모두 다 대문자로 변경 후 문자열 리턴(영문자 및 대소문자를 지원하는 언어에 한정)
(7.2) 문자열.toLowerCase() : String
: 문자열을 모두 다 소문자로 변경 후 리턴.
ex)
String str1 = "Hello World";
System.out.println("upper : " +str1.toUpperCase());
System.out.println("lower : " +str1.toLowerCase());

(8) 문자열.toCharArray() : char[]
: 문자열의 각 문자들을 char[]배열에 옮겨 담은 후 해당 배열을 리턴
ex)
String str1 = "Hello World";
char[] arr = str1.toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));

(9) static valueOf(char[] data) : String
ex)
char[] arr = str1.toCharArray();
System.out.println(String.valueOf(arr));
System.out.println(String.valueOf(1));
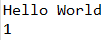
'JAVA > JAVA 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] API 실습 문제 (0) | 2023.10.19 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 11-2. 기본 API(2) (StringTokenizer, StringBuffer, StringBuilder 클래스) (1) | 2023.10.19 |
| [JAVA] 다형성(추상 클래스, 인터페이스 실습) (0) | 2023.10.18 |
| [JAVA] 10-3. 다형성(추상클래스 abstract 와 인터페이스) (0) | 2023.10.18 |
| [JAVA] 10-2. 다형성 객체 배열 실습 2(Book객체) (0) | 2023.10.17 |


